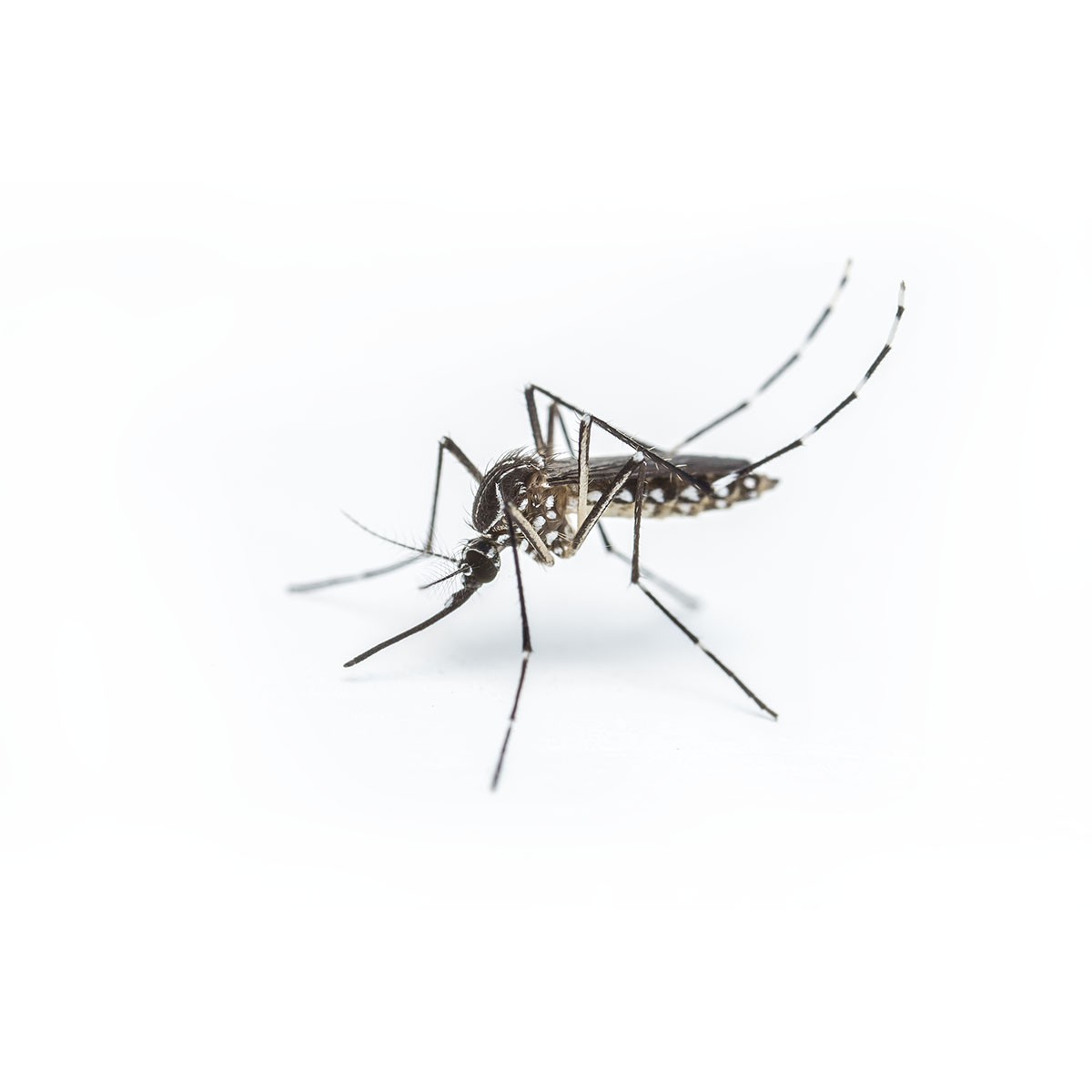
Mosquito
CULEX, AEDES, ANOPHELES ET OCHLEROTATUS SPP.
Identification
The females have a relatively smooth proboscis, while the male’s is feather-like. Their wings are covered with fine scales. There are several similar species. These can be identified by studying the genitals under a microscope.
Size: from 4 to 7 mm. Colour: brown abdomen.
Living Areas
It develops in stagnating or virtually still water. Likes moist environments, leaves, houses and farm buildings. Some species can fly for several kilometres. Active at nightfall and during the night.
Feeding
Adult: the males feed on plant sap, while the female feeds on the blood of animals and humans. Larvae: feed on micro-organisms in water.
Nuisances
Itching and sleepless nights. Possible diseases: Encephalitis from the Culex mosquito, yellow fever from the Aedes mosquito and zika, dengue, malaria from the Anopheles mosquito.
Life Cycle
Larval development: from 5 to 10 days (4 stages). Development cycle: roughly 10 days. Lifecycle: a few weeks. Fertility: one hundred eggs